Key Points
- We expect inflation and interest rates to persist at higher levels than in the previous market regime.
- Alongside this, elevated levels of post-Covid government debt create a drag on economies which, in turn, can lead to broadly more volatile market returns.
- With governments needing to maintain spending on health and defense, the appetite for fiscal policy to support growth is undermined by the interest bill.
- When the market trinity of inflation, debt and interest rates is on the rise, market anxiety rises, as does higher volatility.
- We believe we have entered this phase but there are early signs that calm can return.
It might appear to be stating the obvious, but for markets to be in a good mood, the market ‘trinity’ of inflation, debt and interest rates, all need to be well behaved. All three indicators are connected, of course, but if inflation remains stable and at low levels, interest rates do not need to be too elevated. Meanwhile, if government debt is stable and not too much of a burden, free markets are able to continue investing capital productively.
In this new market regime, we keep talking about how we expect inflation to remain consistently higher than previously and, as a result, interest rates will need to be higher too. Alongside this, elevated levels of post-Covid government debt create a drag on economies which, in turn, can lead to broadly more volatile market returns.
In this blog, we assess the current state of this trinity of market influencers through the lens of our macro themes.
Persistent Inflation
Inflation has been on a rollercoaster ride since the Covid pandemic, driven higher by labor misalignment and energy-price spikes following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the consequent need for energy-supply adjustments. There then followed a downward trend where the energy price effects fell away, only to be replaced by the legacy concerns over higher wage costs. Wage inflation, once entrenched, is always difficult to remove, especially when ageing demographics and spending patterns are creating high demand for labor at the same time as we are seeing a shortage of the right employees.
To control this scenario, central banks need to create an environment in which unemployment rises. Using interest rates to do this can be both blunt and slow. The latest US Employment Cost Index has reminded the market that wage inflation is not coming down; this is unsurprising, given that US employment remains strong and is yet to turn meaningfully. Against this economic backdrop, we believe the US central bank will remain careful not to remove the tight monetary policy too soon. With inflation creeping back up and thereby pushing interest-rate expectations higher again, the market has become anxious once more.
In a previous blog, Market Outlook: A Case of ‘Déjà Vu’, we suggested that this inflationary growth phase would follow the ‘Goldilocks’ market period (where the trinity of market indicators were in line) and that it would lead to market volatility. It appears that we may have now reached this phase.
Human Capital
There is one of our important macro themes at play here: human capital (the change in the type and cost of labor). This theme identifies the change in demographics that causes the shortage of labor, as well as the possibility that companies need to find alternatives. In the previous market regime, labor was relatively cheap and had little influence on the cost of production. Now, with wage growth running at higher levels than inflation, it is expensive, and increases the incentive to invest capital in alternatives (artificial intelligence and robots).
Recent data suggests there is a gradual deterioration in labor hiring, and this will eventually remove the need for higher rates. For the next few months though, we suspect that markets will continue to fret over inflation, with a heightened focus on the level of interest rates and central bank comments.
Government Debt
The third element of the market trinity, government debt, could prove to be important for the longer-term level of markets. Government debt levels have skyrocketed in recent years owing to the need to support the financial system after 2008 and the consumer during the pandemic. With government debt rising to levels not seen since the 1930s, and the cost of servicing that debt also on the rise, should we be concerned about the sustainability of that debt? We believe ‘yes’ is the answer, although there is always a ‘but’.
Our big government theme, which identifies the increased involvement of governments in the running of economies, concludes that high debt levels are here to stay. The post-Covid increase in social spending gave way to an increased focus on the need to be more self-sufficient in energy and supply lines.
General Government Debt Trends for Selected Developed Markets (% of GDP)
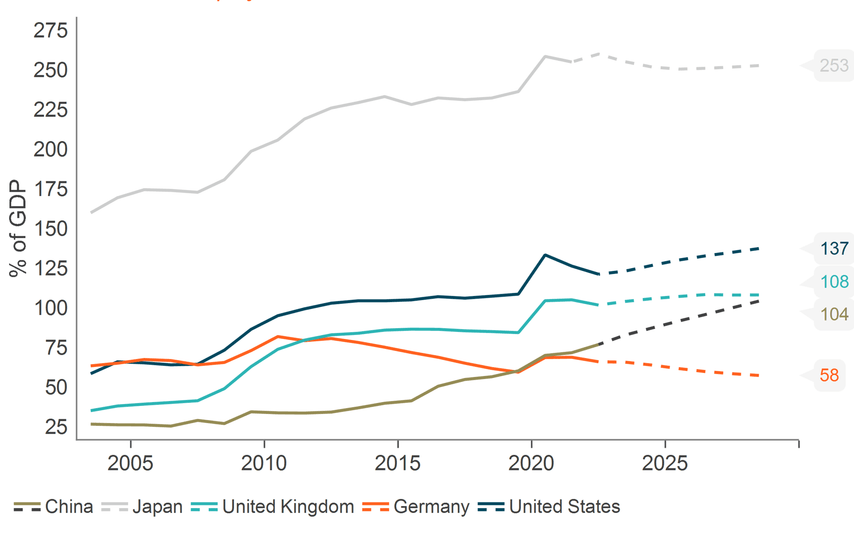
Source: Macrobond, International Monetary Fund Data as of April 5 2024
Furthermore, our geopolitical macro theme great power competition defines a period of heightened conflict resulting in a need for governments to increase defense spending. The chart below shows the change in defense spending for NATO members between 2019 and 2023 as a percentage of GDP.
NATO Defense Expenditure, % of GDP
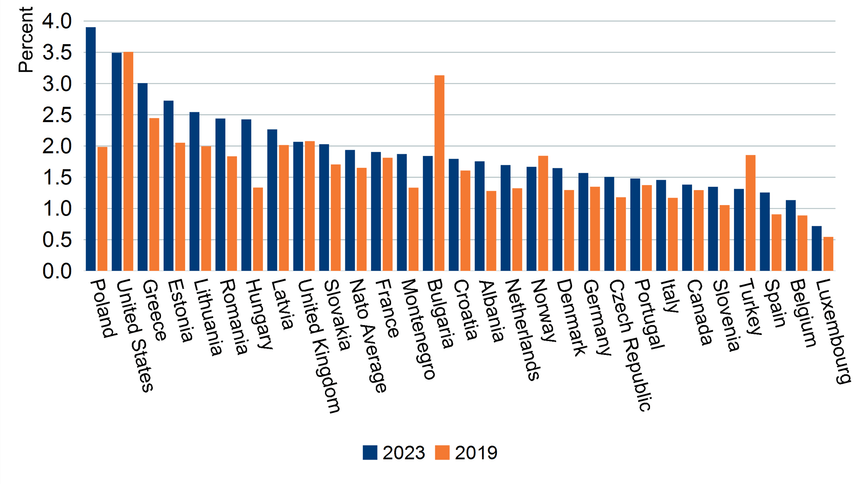
Source: Macrobond and NATO, December 2023
Higher government debt levels may not be all bad news, however, as the offset to an increase in government debt is usually a reduction in private-sector debt. Taking the US as an example, since the 2008 global financial crisis we have seen a reduction in private-sector debt, particularly in financials (a direct response to the banking crisis) and households (which saw increased savings during the Covid pandemic).
Debt Concerns
The concern for the market, though, is that the cost of debt keeps rising and, eventually, governments cannot afford the interest-rate bill. With bond yields set to remain higher for longer (reflecting the higher inflation story), this seems a legitimate concern. In addition, with governments needing to maintain spending on health and defense, the appetite for fiscal policy to support growth is undermined by the interest bill.
Less flexibility on spending plans can result in frequent political change, as successive governments fail to fulfil their electoral policies, and a potential crowding out of other investments. We believe fears might grow that the debt is unsustainable, and investors may start to worry about default.
In the past, high debt levels have been managed through financial repression (post global financial crisis) and by inflating the problem away. If inflation is high, nominal GDP grows rapidly and so too does tax revenue. Ultimately, the debt becomes more affordable. This appears to be the phase we are in now. Meanwhile, forcing domestic investors to buy the bonds issued by the governments is also an approach which allows the debt to find buyers while we wait for inflation to have an impact. In some countries (Japan, for example) this may be required to allow the central banks to stop their bond purchases.
Could Calm Return?
When the market trinity of inflation, debt and interest rates is on the rise, market anxiety rises, as does higher volatility. We believe we have entered this phase but there are early signs that calm can return. Tighter monetary policy is starting to influence employment, thus reducing the need to have higher wages. Unfortunately, it may take some time for headline inflation to resume its downward trend which, in turn, will allow central banks to reduce interest rates. Higher-for-longer inflation and interest rates can raise awareness of the cost of high government debt levels, which also keeps markets nervous. And yet here too, we can see some solutions further down the road. In an upcoming blog, we will delve more deeply into the potential for deflation to become the dominant theme later in the year.
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS. Any reference to a specific security, country or sector should not be construed as a recommendation to buy or sell this security, country or sector. Please note that strategy holdings and positioning are subject to change without notice. MAR006312 Exp 06/29. For additional Important Information, click on the link below. Analysis of themes may vary depending on the type of security, investment rationale and investment strategy. Newton will make investment decisions that are not based on themes and may conclude that other attributes of an investment outweigh the thematic research structure the security has been assigned to.
Important information
This is a financial promotion. Issued by Newton Investment Management Limited, The Bank of New York Mellon Centre, 160 Queen Victoria Street, London, EC4V 4LA. Newton Investment Management Limited is authorized and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority, 12 Endeavour Square, London, E20 1JN and is a subsidiary of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation. 'Newton' and/or 'Newton Investment Management' brand refers to Newton Investment Management Limited. Newton is registered in England No. 01371973. VAT registration number GB: 577 7181 95. Newton is registered with the SEC as an investment adviser under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940. Newton's investment business is described in Form ADV, Part 1 and 2, which can be obtained from the SEC.gov website or obtained upon request. Material in this publication is for general information only. The opinions expressed in this document are those of Newton and should not be construed as investment advice or recommendations for any purchase or sale of any specific security or commodity. Certain information contained herein is based on outside sources believed to be reliable, but its accuracy is not guaranteed. You should consult your advisor to determine whether any particular investment strategy is appropriate. This material is for institutional investors only.
Personnel of certain of our BNY Mellon affiliates may act as: (i) registered representatives of BNY Mellon Securities Corporation (in its capacity as a registered broker-dealer) to offer securities, (ii) officers of the Bank of New York Mellon (a New York chartered bank) to offer bank-maintained collective investment funds, and (iii) Associated Persons of BNY Mellon Securities Corporation (in its capacity as a registered investment adviser) to offer separately managed accounts managed by BNY Mellon Investment Management firms, including Newton and (iv) representatives of Newton Americas, a Division of BNY Mellon Securities Corporation, U.S. Distributor of Newton Investment Management Limited.
Unless you are notified to the contrary, the products and services mentioned are not insured by the FDIC (or by any governmental entity) and are not guaranteed by or obligations of The Bank of New York or any of its affiliates. The Bank of New York assumes no responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the above data and disclaims all expressed or implied warranties in connection therewith. © 2020 The Bank of New York Company, Inc. All rights reserved.
In Canada, Newton Investment Management Limited is availing itself of the International Adviser Exemption (IAE) in the following Provinces: Alberta, British Columbia, Ontario and Quebec and the foreign commodity trading advisor exemption in Ontario. The IAE is in compliance with National Instrument 31-103, Registration Requirements, Exemptions and Ongoing Registrant Obligations.





